Use the following to answer questions
Scenario III
Scenario III is based on fabricated data inspired by the following study:
Spencer, S. J., Steele, C. M. & Quinn, D. M. (1999) . Stereotype threat and women's math performance. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 35, 4-28.
Effect of Stereotype Threat on Math Study
The myth that men outperform women in math is widely believed by many individuals. The purpose of the study described in Scenario III was to determine if a sample of women whose math abilities equaled a sample of men would fall victim to this threat. To that end, 28 adult men and 28 adult women were administered an easy math test or a difficult math test. The performance of men and women on both the easy and hard test was quantified. A two-factor ANOVA revealed a significant main effect for test, with participants scoring significantly better on the easy test. The analyses also revealed a main effect for sex, with men performing significantly better than women. The interaction between test difficulty and sex was also statistically significant. Further inspection of the data revealed that although men and women did not differ on the easy math test, women performed significantly less well than men on the difficult math test. Given that the screening criteria for participants including earning a grade of B or better in college calculus, and scoring in at least the 85th percentile on the math subsection of the ACT, the current study indicates that women do succumb to math stereotype threat but only when the math challenge is great. The data are presented in Figure 2.
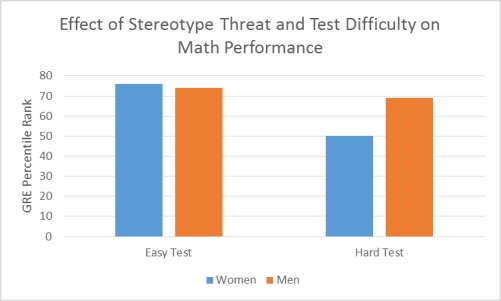 Figure 2. Although women and men performed equally on an easy version of the math test, women performed significantly worse than men on the difficult version.
Figure 2. Although women and men performed equally on an easy version of the math test, women performed significantly worse than men on the difficult version.
-(Scenario III) The study described in Scenario III used a factorial design to examine the effect of sex and test difficulty on math performance. Which of the following is NOT true of factorial designs?
Definitions:
Experimenter Bias
The influence of the researcher's expectations or personal beliefs on the outcomes of an experiment.
Subject Bias
A tendency for participants in research to respond or behave in a certain way because they are aware they are being studied.
Confounds
Variables that are external to the experimental design itself and can affect the results, thereby casting doubt on the reliability of the conclusions.
Selection Bias
A distortion in statistical analysis resulting from the method of collecting samples.
Q4: Dr. Tonn emphasized in class that the
Q27: A single-subject design is a special type
Q51: (Scenario III) Scenario III describes that only
Q67: A t-test for independent means is appropriate
Q80: _ is a statistical test in which
Q89: The current Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of
Q91: Process evaluation has several noted purposes, including
Q95: A double-blind procedure is used in an
Q146: Dr. Domnica conducted a mixed design ANOVA
Q154: Dr. Carlos specifies in his statistical methodology