Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
Scenario I is based on fabricated data inspired by the following study:
Curry, N. A. & Kasser, T. (2005) . Can coloring mandalas reduce anxiety? Art Therapy: Journal of American Art Therapy Association, 22(2) 81-85.
Effect of Coloring on Anxiety
Curry and Kasser were interested in examining whether coloring complex geometric patterns reduces anxiety. To that end, they induced anxiety in 84 undergraduate volunteers from their university. Following anxiety induction the participants were divided into two coloring conditions. To determine which condition each participant would be in the researchers put all of their names in a hat. The first name drawn was placed in group 1, the second name drawn was placed in group 2, the third name drawn was placed in group 1, and so on. Those in the complex geometric coloring condition (group 1) were given a paper with a plaid pattern or the outline of a mandala. Those in the control condition (group 2) were given a blank piece of paper. After 20 minutes of coloring all of the participants completed a self-administered State Anxiety Inventory (SAI) . Lower SAI scores indicate low levels of anxiety whereas higher SAI scores indicate high levels of anxiety. The mean SAI scores of each coloring condition were compared to determine whether the type of coloring one does affects anxiety. The results revealed that those who colored a complex geometric pattern had significantly different levels of anxiety than those who colored on a blank sheet of paper. Curry and Kasser concluded that coloring causes a change in anxiety, but only when coloring requires a certain amount of attention and focus.
Figure 1. Effect of Coloring on Anxiety
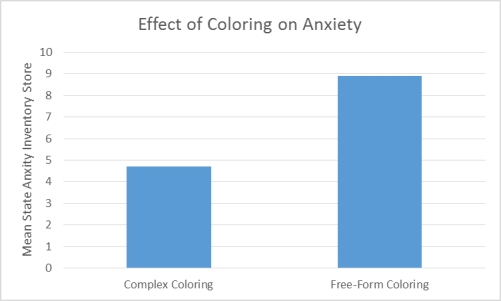
-(Scenario I) Based on the information provided in Scenario I, which of the following statements BEST describe(s) the data shown in Figure 1?
Definitions:
African American Students
Pupils of African descent in the United States who encounter unique educational experiences and challenges shaped by various socio-cultural and historical factors.
European American Students
Refers to learners in educational institutions in the United States who have European ancestry.
Intrinsically Oriented
Intrinsically Oriented refers to being motivated by internal factors, such as personal satisfaction, curiosity, or the challenge of the task itself, rather than external rewards or pressures.
External Rewards
Incentives provided from an external source, such as money, grades, or praise, that motivate behavior.
Q22: Describe how today's reality television shows lack
Q25: Tambra needs to make sure that she
Q70: Camila is interested in examining whether people
Q80: _ is a statistical test in which
Q88: _ is any way that the interviewer
Q97: Dr. Alier is examining psychopathic tendencies among
Q117: A _ focuses on a within-subjects design
Q128: To establish a scale's construct validity researchers
Q168: Dr. Toy was interested in examining two
Q168: A(n) _ is a statistic used to