Exhibit 7.2
The following questions are based on the problem below.
An investor has $150,000 to invest in investments A and B. Investment A requires a $10,000 minimum investment, pays a return of 12% and has a risk factor of .50. Investment B requires a $15,000 minimum investment, pays a return of 10% and has a risk factor of .20. The investor wants to maximize the return while minimizing the risk of the portfolio. The following multi-objective linear programming (MOLP) has been solved in Excel. 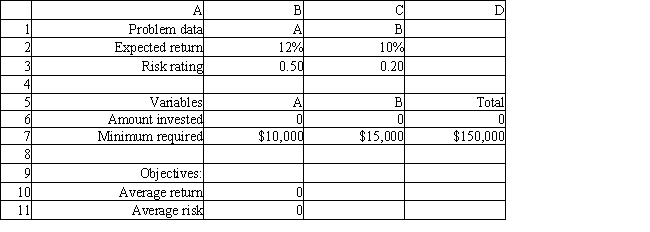
-Refer to Exhibit 7.2. What formula goes in cell B10?
Definitions:
Marginal Cost
Marginal cost is the increase in total cost that arises from producing one additional unit of a product or service.
Total Variable Costs
The sum of all costs that vary directly with the level of production, such as materials and labor directly involved in the production process.
Supply Curve
A graphical representation showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of that good that suppliers are willing to sell.
Production Functions
Mathematical relationships expressing the output of a firm, an industry, or an entire economy as a function of inputs.
Q4: Which of the following is true of
Q35: Refer to Exhibit 3.5. What formula could
Q42: A cellular phone company wants to locate
Q44: The optimal trade-off between risk and return
Q47: Refer to Exhibit 9.1. Interpret the meaning
Q48: Decision-making problems which can be stated as
Q62: A technique that analyzes past behavior of
Q75: In modeling a problem it is usually
Q92: Draw the network representation of this LP
Q109: One element in cleaning the data set