Exhibit 7.4
The following questions are based on the problem below.
Robert Gardner runs a small, local-only delivery service. His fleet consists of three smaller panel trucks. He recently accepted a contract to deliver 12 shipping boxes of goods for delivery to 12 different customers. The box weights are: 210, 160, 320, 90, 110, 70, 410, 260, 170, 240, 80 and 180 for boxes 1 through 12, respectively. Since each truck differs each truck has different load capacities as given below: 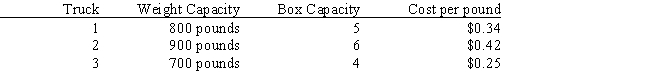 Robert would like each truck equally loaded, both in terms of number of boxes and in terms of total weight, while minimizing his shipping costs. Assume a cost of $50 per item for trucks carrying extra boxes and $0.10 per pound cost for trucks carrying less weight.
Robert would like each truck equally loaded, both in terms of number of boxes and in terms of total weight, while minimizing his shipping costs. Assume a cost of $50 per item for trucks carrying extra boxes and $0.10 per pound cost for trucks carrying less weight.
The following integer goal programming formulation applies to his problem.
Y1 = weight loaded in truck 1; Y2 = weight loaded in truck 2; Y3 = weight loaded in truck 3;
Xi,j = 0 if truck i not loaded with box j; 1 if truck i loaded with box j.  Given the following spreadsheet solution of this integer goal programming formulation, answer the following questions.
Given the following spreadsheet solution of this integer goal programming formulation, answer the following questions. 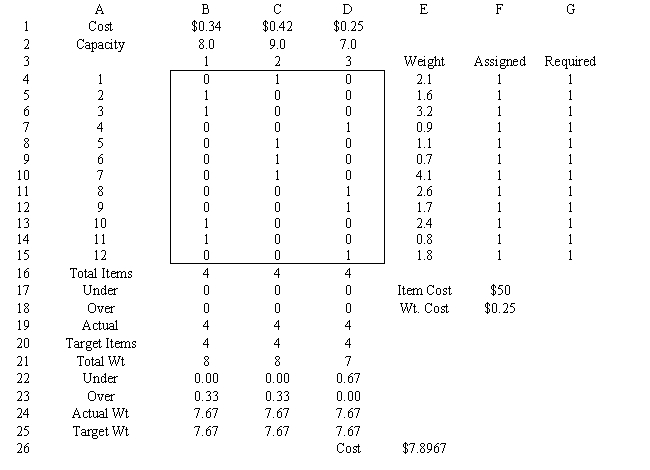
-Refer to Exhibit 7.4. Based on the integer goal programming formulation, the associated solution, and spreadsheet model, what formulas should go in cells B19:E19 and B24:E24 of the spreadsheet?
Definitions:
Sacrifice Ratio
An economic term that quantifies the effect of decreasing inflation on an economy, typically measured as the percentage loss in output per one percentage point decrease in inflation.
Housing and Financial Crisis
A period characterized by declining home prices, foreclosures, and a loss of value in financial instruments, leading to widespread economic instability.
World Prices
The prices of goods and services determined in the global market that influence the cost and availability of products internationally.
Aggregate Demand
The total amount of goods and services demanded in an economy at a given overall price level and time.
Q1: The main difference between shadow prices and
Q5: A company wants to purchase large and
Q14: Consider the formulation below. How many decision
Q22: Given the following Analytic Solver Platform sensitivity
Q34: Refer to Exhibit 11.8. What formula should
Q41: The difference between the right-hand side (RHS)
Q54: Which method is preferred for solving fully
Q92: Refer to Exhibit 3.2. Which of the
Q99: A company produces three products which must
Q101: Refer to Exhibit 11.24. Based on the