Exhibit 12.4.
The following questions use the information below.
The manager of a Washington, DC sightseeing tour company is concerned about overbooking for one of his bus tours. The bus has 15 seats but sometimes there are empty seats. His records show that about 20% of ticket holders do not show up for their tour. Tickets cost $10 and are non-refundable. If the manager overbooks the tour and more than 15 passengers show up, some of them will be bumped to a later tour. This bumping costs the company $25 in various expenses to keep the customer happy until the next tour. The manager wants to see what happens to profits if 18 reservations are accepted. 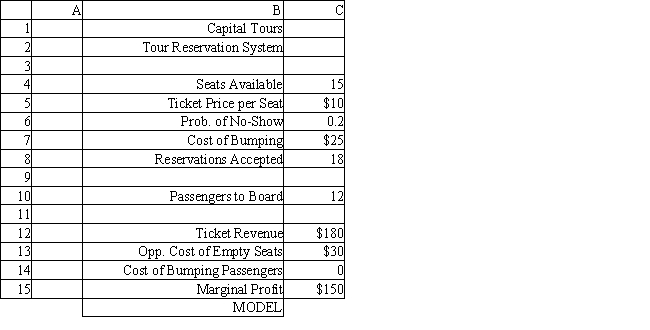
-Using the information in Exhibit 12.4, what formula should go in cell C13 of the worksheet to determine the Opportunity Cost of Empty Seats?
Definitions:
Performance Determinants
Performance determinants are factors that can influence an individual's or organization's ability to achieve objectives, including skills, resources, and external conditions.
Flexible Leadership Theory
A theory suggesting organizations can achieve success through adaptable leadership practices tailored to operational requirements, change, and efficiency.
External Environment
All factors outside an organization that can potentially affect its performance and operations.
Volatile
Characterized by rapid, unexpected changes or instability, often associated with financial markets, chemicals, or situations.
Q3: Resistance to attack using self-defense is justified
Q5: An office supply company is attempting to
Q17: Restorative justice seeks recovery of the victim
Q23: The average demand is 4.45 cases per
Q51: In discriminant analysis the averages for the
Q51: Refer to Exhibit 11.6. What formula should
Q64: The critical path is the _ path
Q71: Using the information in Exhibit 12.3, what
Q80: In classification techniques the dependent variable is<br>A)
Q100: The decision rule which selects the alternative