Somani Corporation has an activity-based costing system with three activity cost pools-Machining, Setting Up, and Other. The company's overhead costs, which consist of equipment depreciation and indirect labor, have been allocated to the cost pools already and are provided in the table below. 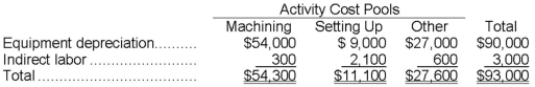 Costs in the Machining cost pool are assigned to products based on machine-hours (MHs) and costs in the Setting Up cost pool are assigned to products based on the number of batches. Costs in the Other cost pool are not assigned to products. Data concerning the two products and the company's costs appear below:
Costs in the Machining cost pool are assigned to products based on machine-hours (MHs) and costs in the Setting Up cost pool are assigned to products based on the number of batches. Costs in the Other cost pool are not assigned to products. Data concerning the two products and the company's costs appear below: 
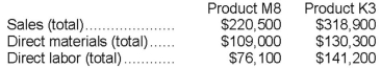 Required:
Required:
a. Calculate activity rates for each activity cost pool using activity-based costing.
b. Determine the amount of overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using activity-based costing.
c. Determine the product margins for each product using activity-based costing.
Definitions:
Tariff
A tax imposed by a government on goods and services imported from other countries to protect domestic industries from foreign competition.
Domestic Price
The price of goods or services within a country's borders, as opposed to international or export prices.
Tariff
A tax imposed by a government on imported or exported goods, often used to restrict trade, as they increase the price of imported or exported goods, making them less attractive to consumers.
Consumer Surplus
The difference between the total amount consumers are willing to pay for a product or service and the total amount they actually pay.
Q3: How much supervisory wages and salaries and
Q4: While making decisions, Jason selects the alternative
Q5: The company's overall break-even sales is closest
Q10: Objectives should _.<br>A) be specific<br>B) have a
Q20: John is a middle manager. He chooses
Q22: Buentello Corporation produces and sells a single
Q28: One of the critical pieces of the
Q72: Activity rates are computed in the second-stage
Q76: Reynold Enterprises sells a single product for
Q196: Craft Corporation produces a single product. Last