The figure below shows the demand (D) and supply (S) curves of cocoa in the U.S.Figure 21.4
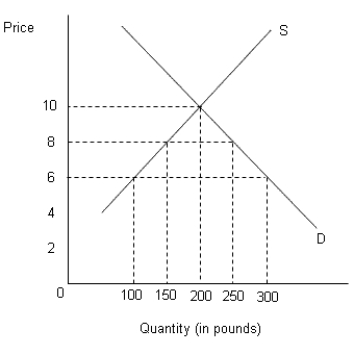
-Creating conditions for fair trade by limiting imports will make the domestic consumers better off as they will be required to pay low prices for the products.
Definitions:
Price Discrimination
The strategy of selling the same product or service at different prices to different groups of consumers, based on their willingness or ability to pay.
Profits
The financial gain obtained when revenues from sales exceed the costs associated with production and selling the goods or services.
Perfect Price Discrimination
The price discrimination that results when a monopolist charges each consumer the maximum that the consumer is willing to pay.
Marginal Cost
The change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented by one unit.
Q2: The supply curve in the market for
Q6: Unlike nonrenewable resources, the timing of extraction
Q35: In the market for both renewable and
Q51: Consumers make all economic decisions in a
Q53: If the world price is above the
Q71: The official poverty-line income is adjusted annually
Q74: The principle of comparative advantage states that
Q83: Health care can be regarded as a(n):<br>A)normal
Q84: If you receive a dollar return of
Q423: Markets promote<br>A)equity and competition.<br>B)voluntary exchange and equality.<br>C)equity