The following table shows the marginal revenues earned by a price discriminating monopolist from two different markets. Table 24.4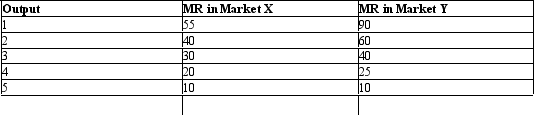 Refer to Table 24.4.How would a price-discriminating monopolist allocate his or her product between market X and market Y if marginal cost is $40 in both markets?
Refer to Table 24.4.How would a price-discriminating monopolist allocate his or her product between market X and market Y if marginal cost is $40 in both markets?
Definitions:
Par Value
The nominal or face value of a stock or bond, as stated by the issuing company, that has no direct correlation to the market value.
Corporate Existence
The state of being recognized as a legal entity that is separate from its owners, enabling the corporation to own assets, incur liabilities, and enter into contracts.
Business Combination
A transaction or other event in which an acquirer obtains control of one or more businesses.
Common Stock
Equity ownership in a corporation, giving shareholders voting rights and a share in the company's profits through dividends.
Q16: The figure below shows revenue and cost
Q21: When the commons are converted into privately
Q35: A cartel attempts to increase profits in
Q44: If the official gold value of the
Q46: Appreciation of the dollar means that now
Q61: The figure given below shows the aggregate
Q63: Why is a perfectly competitive firm said
Q82: If barriers to entry exist in a
Q83: A monopolist's demand curve is less elastic
Q115: A perfectly competitive firm spends a significant