The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
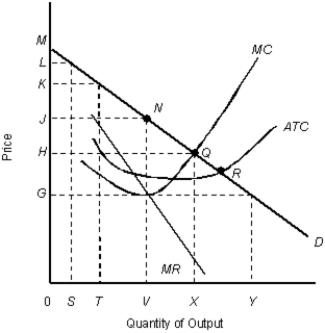 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-A monopolist can charge whatever price it wants and can therefore reap phenomenal profits.
Definitions:
Acquired Comparative Advantage
Acquired comparative advantage refers to the benefits a country develops over time through investment, innovation, and improvements in skills and technology, as opposed to advantages due to natural resources or geographic location.
United States
A federal republic consisting of 50 states and a federal district, known for its significant global economic, cultural, and political influence.
Agricultural Products
Items produced from farming and agriculture, including crops, livestock, and other consumable items.
Human Capital
The capabilities, insights, and expertise held by a person or a group of people, considered in relation to their worth or expense to a company or nation.
Q1: The exchange-rate arrangement that emerged from the
Q1: The figure given below shows the revenue
Q9: When practicing price discrimination, a firm can
Q23: One of the advantages of floating exchange
Q29: In long-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm:<br>A)will
Q30: If a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm is
Q58: A monopolist can charge a high price
Q73: The free rider problem arises when a
Q80: A market in which adverse selection occurs
Q95: A firm such as a public utility,