The figure given below shows the demand and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm. Figure: 23.4 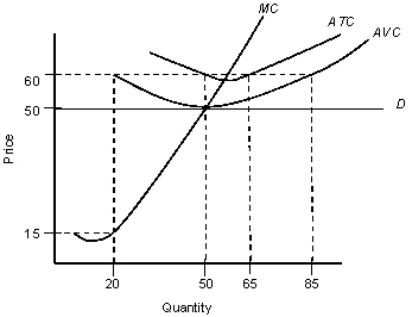 D: Demand curve
D: Demand curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
ATC: Average-total cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
Refer to Figure 23.4.The presence of the average-variable-cost curve suggests that the firm is operating:
Definitions:
Investment Model
Theory that uses three factors—satisfaction, alternatives, and investments—to explain why people stay with their long-term relationship partners.
Sunk Costs
Costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered, which should not influence future decisions but often do.
Alternatives
Different options or choices available in any given situation or decision-making process.
Longitudinal Studies
Research methods that involve observations of the same subjects over a period, often years or decades, to determine long-term effects or trends.
Q6: Why does network externality arise?<br>A)Each additional unit
Q16: According to economists, which of the following
Q26: The perfectly competitive market structure results in
Q44: As the confectionary, Mrs.Fields' Cookies, gained popularity
Q60: A perfectly competitive firm incurs loss in
Q63: Entry of new firms to the industry
Q79: Which of the following statements characterizes perfect
Q80: Since the beginning of the millennium, the
Q104: If a firm has constant returns to
Q109: Fixed exchange rates allow countries to formulate