The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm. Figure 23.2 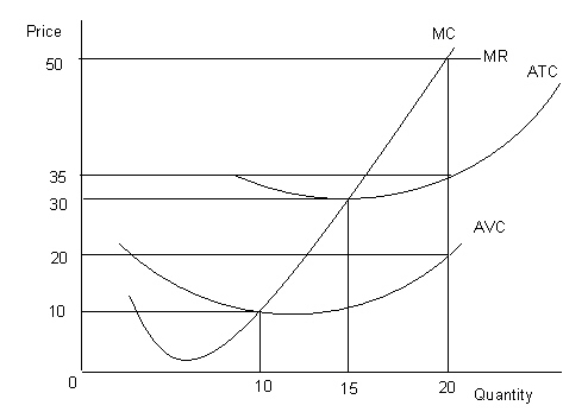 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
Refer to Figure 23.2.If the marginal-revenue curve would have intersected the average-total-cost curve at its lowest point and the firm maximized profit, then total revenue would have been equal to:
Definitions:
Check Amount
The total sum of money written on a check that is payable to the recipient.
Book Balance
The balance in a company's accounting records for a particular account, which may differ from the actual cash balance until reconciled.
Purchasing Department
A division within a company responsible for acquiring goods and services needed for its operations.
Purchase Order
A document issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating the types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services.
Q12: The following graph shows the demand and
Q25: The figure given below depicts the negatively
Q29: A price discriminating monopolist charges a very
Q40: The figure given below depicts the negatively
Q51: How many U.S.dollars does a U.S.importer need
Q66: By forming a cartel the member firms
Q77: The long-run average total cost curve connects
Q98: In the following figure, the first panel
Q101: Perfect competition provides one model in which
Q111: The figure given below shows the demand