The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm. Figure 23.2 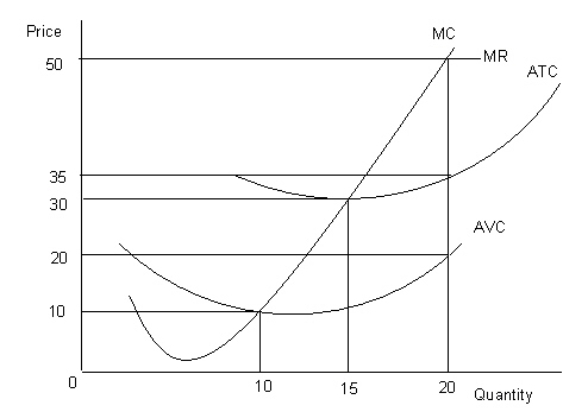 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
Refer to Figure 23.2.If the marginal-revenue curve would have intersected the average-total-cost curve at the latter's lowest point and the firm maximized profit, then total profit would have been equal to:
Definitions:
Confidence Level
The percentage or degree of confidence that a parameter lies within a specified range, usually associated with confidence intervals in statistics.
Sample Size
The number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample.
Population Standard Deviation
A measure of the dispersion or variability of a set of data points in a population, denoting how spread out the data points are from the mean of the population.
Sample Size
The number of observations or units collected in a study or used in statistical analysis.
Q1: The figures given below represent the revenue
Q23: One of the advantages of floating exchange
Q23: The figure given below shows the revenue
Q30: In long-run equilibrium, each monopolistically competitive firm
Q30: The figure given below shows the revenue
Q32: Although the GATT was supported by most
Q37: Which of the following countries is forbidden
Q44: As the confectionary, Mrs.Fields' Cookies, gained popularity
Q47: A firm maximizes its profit at a
Q65: Since a firm is willing to sell