The figures given below represent the revenue curves of a monopolist. Figure 10.2 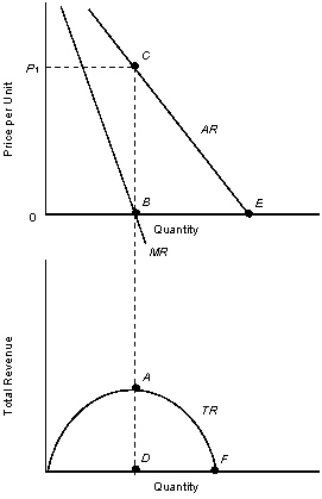 TR: Total revenue curve
TR: Total revenue curve
AR: Average revenue curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
Refer to Figure 10.2.In order to maximize profits, what quantity should the monopolist produce?
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in market stability.
Tax Revenues
The financial resources that are accumulated by governments as a result of taxation.
Producer Surplus
The discrepancy between the price at which sellers are prepared to offer a product and the actual price they end up getting.
Consumer Surplus
The difference in total payment consumers are able and willing to offer for a good or service, compared to the payment they actually provide.
Q5: Assume an economy has automatic stabilizers in
Q6: Increased domestic imports and higher international trade
Q18: Money fails to act as a store
Q20: If a monopolist is producing at that
Q39: An increase in the reserve requirement from
Q43: When regulators require that a natural monopoly
Q52: The following figure shows equilibrium at the
Q72: The sum of consumption and saving is
Q100: Which of the following statements best describes
Q102: If market demand increases, a perfectly competitive