The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
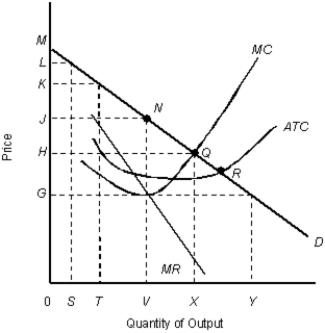 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-Economies of scale, control over a scarce input, and patents are all examples of barriers to entry.
Definitions:
Complement Method
A technique used in mathematics to find the complement of a set or in digital electronics to simplify calculations.
Trade Discount
A reduction in the retail price of goods or services offered to wholesalers or those buying in bulk, often based on volume or quantity purchased.
Net Price
The actual price paid for a product or service after all discounts, rebates, and other reductions have been applied.
Discount Method
A financial calculation technique used to determine the present value of future cash flows or payments by applying a specific discount rate.
Q1: Which of the following can be categorized
Q9: The table given below shows the total
Q17: Ceteris paribus, if the U.S.federal government reduces
Q46: If the monopolist's price happens to be
Q50: An MPI of 0.4 indicates that for
Q58: If equilibrium in the economy is merely
Q73: A firm such as a public utility,
Q76: _ is the primary determinant of consumption
Q97: The Keynesian aggregate expenditures model assumes that
Q112: A perfectly competitive firm produces 50 units