The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Figure 10.2
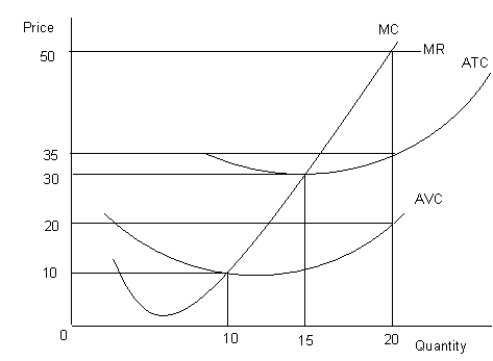 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
-In the short run, a firm continues to produce only if it can cover the:
Definitions:
Total Revenues
The total amount of money generated by a firm from its sales activities before any expenses are subtracted.
Elastic
A description of a variable's sensitivity to change in another variable, often used in economics to describe how demand or supply responds to changes in price.
Price-elasticity Coefficient
A measure that calculates how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in its price, quantitatively.
Revenues
The total income generated by a company from its business operations, such as sales of goods or services, before any costs or expenses are deducted.
Q15: In which market structure model(s)is product differentiation
Q30: A higher domestic price level lowers aggregate
Q31: Suppose an increase in investment spending results
Q44: The following table shows the units of
Q58: The table below shows the payoff (profit)matrix
Q60: Which among the following does not determine
Q83: The table given below reports the marginal
Q95: If people expect the economy to do
Q98: The consumption function becomes flatter if:<br>A)the average
Q100: When firms in an illegal market form