Scenario 6-2
Suppose demand for a product is given by the equation 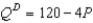 and supply for the product is given by the equation
and supply for the product is given by the equation 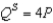
-Refer to Scenario 6-2. Suppose the government sets a price floor at $13 for this product. Initially, is this price floor binding? Suppose that for some reason demand were to decrease to 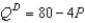 Would the $13 price floor be binding after the shift in the demand curve? If so, what is the size of the resulting shortage/surplus?
Would the $13 price floor be binding after the shift in the demand curve? If so, what is the size of the resulting shortage/surplus?
Definitions:
Setting Objectives
The process of establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals for an individual, team, or organization.
Operational Planning
The process of setting short-term objectives and determining the best methods to achieve them within the framework of the organization's overall strategic plan.
Intermediate Planning
A type of planning that focuses on setting objectives and strategies for a mid-term period, balancing between long-term visions and short-term actions.
Planning/Control Cycle
A continuous process in organizations that involves planning for future activities, executing plans, monitoring results, and making adjustments as necessary.
Q14: Lawmakers designed the burden of the FICA
Q42: If a tax is levied on the
Q152: Celine buys a new MP3 player for
Q272: Refer to Figure 7-26. At the equilibrium
Q371: Refer to Table 7-9. The price that
Q401: Refer to Figure 6-20. Suppose a tax
Q418: The minimum wage does not apply to<br>A)
Q494: Refer to Figure 6-23. Which of the
Q550: Define a price floor.
Q648: Economic policies often have effects that their