The decision tree depicts two players (Jane and Aaron) playing an ultimatum game where Aaron is given $1,000 and asked to propose a way of splitting it with Jane. When Jane learns Aaron’s proposal, Jane chooses whether to accept or reject the split. If Jane accepts the split, both players receive the money according to Aaron’s split proposal. If Jane rejects the split, both players receive nothing. This game will be played only once, so Aaron does not have to worry about reciprocity when making his choice.
There are four sets of payoffs at the terminal nodes of the decision tree. In each node, the dollar amount to the left of the comma represents Aaron’s payoff, and the dollar amount to the right of the comma represents Jane’s payoff.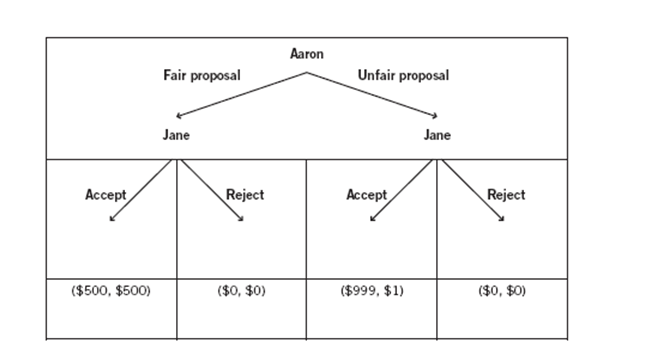
-If Aaron could be 100% certain that Jane was rational, did not care about fairness, and always made decisions to maximize her payoff regardless of the situation she might find herself in, Aaron would likely offer a(n) :
Definitions:
Awkward References
Unclear or poorly made citations in text that disrupt the flow or understanding.
Camouflaged Verbs
Verbs that are made to blend into a sentence by being transformed into a noun or adjective form, potentially obscuring action.
Dangling Modifiers
Words or phrases that do not clearly attach to the words they modify, causing confusion.
Bullets
Small symbols often used in written documents to organize, highlight, or emphasize key points in a list.
Q12: Behavioral economics seeks to dethrone _ and
Q18: An example of a direct negative incentive
Q22: Due to the fact that firms concern
Q46: When a third firm enters a market
Q48: Why is it important to adjust the
Q56: Suppose that, in an experimental setting, 100
Q79: What is the value of additional output
Q81: Thomas Malthus's prediction of mass starvation failed
Q90: In a single-payer system, which of the
Q118: Aïee! ("ouch!" in French). I'm a retired