The decision tree depicts two players (Jane and Aaron) playing an ultimatum game where Aaron is given $1,000 and asked to propose a way of splitting it with Jane. When Jane learns Aaron’s proposal, Jane chooses whether to accept or reject the split. If Jane accepts the split, both players receive the money according to Aaron’s split proposal. If Jane rejects the split, both players receive nothing. This game will be played only once, so Aaron does not have to worry about reciprocity when making his choice.
There are four sets of payoffs at the terminal nodes of the decision tree. In each node, the dollar amount to the left of the comma represents Aaron’s payoff, and the dollar amount to the right of the comma represents Jane’s payoff.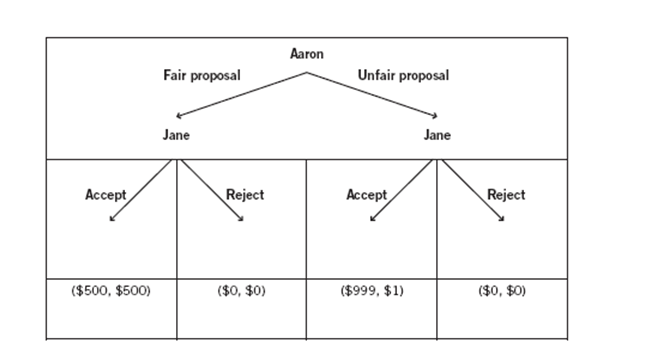
-If Aaron could be 100% certain that Jane was rational, did not care about fairness, and always made decisions to maximize her payoff regardless of the situation she might find herself in, Aaron would likely offer a(n) :
Definitions:
Total Benefit
The complete gain or advantage that an individual, entity, or society receives from consuming a good or service.
Football Games
Competitive sporting events involving two teams aiming to score points by moving a ball into the opposing team's end area, primarily through kicking, carrying, or passing.
Marginal Benefit
The extra pleasure or benefit derived from consuming an additional unit of a product or service.
Marginal Cost
The cost of producing one additional unit of a product.
Q16: The backward-bending labor supply curve occurs because
Q39: Refer to the following indifference curve: <img
Q49: Which of the following represents an accurate
Q65: If the contestant does not change
Q67: Which of the following statements is true?<br>A)
Q76: In 2000, researchers Brigitte Madrian and Dennis
Q93: Suppose that, in an experimental setting, 100
Q105: Refer to the accompanying figure. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4868/.jpg"
Q106: Choose the graph that represents the following
Q134: In the movie A Knight's Tale, three