An executive has been offered a compensation package that includes stock options. The current stock price is $30/share, and she has been offered a call option on 2000 shares, which can be exercised five years from now at a price of $42/share. Therefore, if the market price of the shares in five years is more than $42/share, she can buy 2000 shares at $42/share, and then immediately sell the shares at the market price, earning a riskless profit. If the market price of the shares was less than $42/share, she will obviously choose not to exercise the option, and would have zero profit.
Assume the price of the stock can be modeled as exponential growth (compounding), which could be calculated as: 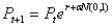 where,
where, 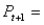 stock price in next period (i.e., price next year)
stock price in next period (i.e., price next year) 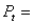 current stock price
current stock price 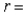 annual growth rate of the stock price, which has been 10%
annual growth rate of the stock price, which has been 10% 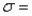 annual volatility, which is estimated to be 18%
annual volatility, which is estimated to be 18% 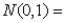 normal random variable with mean of zero and standard deviation of 1
normal random variable with mean of zero and standard deviation of 1
-Simulate the price of the stock in five years by calculating five annual increments (steps) with this model, starting from the current price of $30/share. For each price simulated five years from now, model the exercise decision and calculate the resulting profit, which should then be discounted for five years at the current discount rate (5%) to obtain the present value of the options. What is the expected value of the stock options?
Definitions:
Carbonate Rocks
Sedimentary rocks composed primarily of carbonate minerals, such as limestone and dolomite, often formed from the accumulation of marine organisms' shells.
Wet Environments
Areas characterized by high moisture levels, which can significantly influence local ecosystems and geology.
Clastic Sedimentary Rocks
Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and lithification of mechanical weathering debris, consisting mostly of fragments of older rocks.
Sociotechnical
Relating to the interaction between social and technical elements within an organization, focusing on the relationships between people and technology in work environments.
Q9: Which of the following statements is true
Q15: A(n)database is used by an organization and
Q15: Which of the following is a specialization
Q34: Briefly explain why designing the plant for
Q37: The divisibility property of linear programming means
Q39: Relational algebra defines the theoretical way of
Q40: The covariance is not used as much
Q64: _ provide a description of the data
Q70: A backward procedure is a type of
Q75: The appropriate hypothesis test for an ANOVA