A post office requires different numbers of full-time employees on different days of the week. The number of full-time employees required each day is given in the table below. 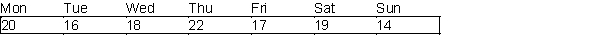 Union rules state that each full-time employee must work five consecutive days and then receive two days off. The post office wants to meet its daily requirements using only full-time employees. Its objective is to minimize the number of full-time employees that must be hired.
Union rules state that each full-time employee must work five consecutive days and then receive two days off. The post office wants to meet its daily requirements using only full-time employees. Its objective is to minimize the number of full-time employees that must be hired.
-(A) Use Solver to formulate and solve the post office's problem.
(B) Suppose the post office has 30 full-time employees and is not allowed to hire or fire any employees. Determine a schedule that maximizes the number of weekend days off received by the employees.
Definitions:
Cocaine Molecule
The cocaine molecule is an organic compound with a complex structure that acts as a powerful stimulant in humans.
Polarity
A property of molecules showing the distribution of electrical charge, leading to molecules having a positive end and a negative end.
Lock And Key Model
A model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes that fit exactly into one another.
Molecular Structure
The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule, determining its chemical properties and behavior.
Q8: When there is a problem with Solver
Q8: Econometric forecasting models,also called causal models,use regression
Q22: Suppose Amanda will stop investing in the
Q24: A noun in a business rule translates
Q33: When the scatterplot appears as a shapeless
Q56: Participation is if one entity occurrence does
Q57: (A)Use simulation to determine how many cars
Q65: According to Codd's rule of relational database,"Application
Q84: A linear programming problem with only decision
Q92: In regression analysis,we can often use the