The joint probabilities shown in a table with two rows, 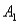 and
and 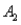 and two columns,
and two columns, 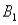 and
and 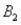 ,are as follows: P(
,are as follows: P( 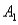 and
and 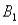 ) = .10,P(
) = .10,P( 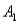 and
and 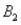 ) = .30,P(
) = .30,P( 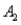 and
and 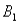 ) = .05,and P(
) = .05,and P( 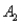 and
and 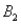 ) = .55.Then P(
) = .55.Then P( 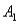 |
| 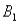 ) ,calculated up to two decimals,is
) ,calculated up to two decimals,is
Definitions:
Informed Consent
A process ensuring that a participant is fully aware of the potential risks and benefits involved in a procedure or experiment before agreeing to partake.
Research Ethics
The moral principles that guide the conduct of scientific research, focusing on issues such as integrity, respect, and responsibility.
Experimental Validity
The extent to which a study accurately reflects or assesses the specific concept that the researcher is attempting to measure.
Counterbalance
Counterbalance refers to a method used to reduce bias in experimental design by varying the order of conditions among participants to even out potential confounding variables.
Q13: (A)Use the sample data to generate a
Q19: The probability of being chosen in a
Q22: A null hypothesis is a statement about
Q27: Which is a common characteristic of the
Q52: After calculating the sample size needed to
Q73: If x is a monetary value (a
Q81: If the sample is a good representation
Q84: Give an example of a simple event.
Q89: Formulate a payoff table that specifies WTC's
Q96: Suppose A and B are mutually exclusive