What does this figure tell about the differences in extinction probabilities between planktotrophic and nonplanktotrophic species? Planktotrophic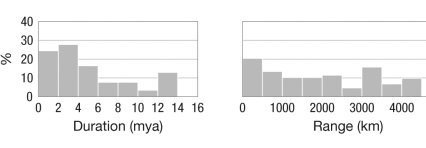
Nonplanktotrophic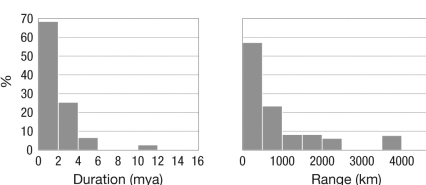
Definitions:
Probation
A period of supervision over an offender, ordered by a court instead of serving time in prison, allowing the person to remain in the community under specific conditions.
Conditional Sentence
A form of judicial punishment that allows an offender to serve a sentence outside of custody, under specific conditions.
Wireless Internet
A method of accessing the internet without the need for physical connections, using radiofrequency waves to transmit data.
Capital Illinois
Springfield, the city designated as the state capital of Illinois, USA.
Q2: The substantial similarity of the AICPA and
Q4: Eukaryotes share<br>A) all of their genes with
Q10: The transition from unicellularity to multicellularity<br>A) has
Q17: The Acts Discreditable Rule states that the
Q22: Regulatory _ are DNA sequences that turn
Q23: Calculate the coefficient of relatedness for the
Q29: In Kohlberg's Six Stages of Moral Development,
Q36: The graph shows the extinction rates for
Q46: Briefly describe reproductive isolation via changes in
Q47: The study of phylogeny predominantly aims to<br>A)