Figure 8-15 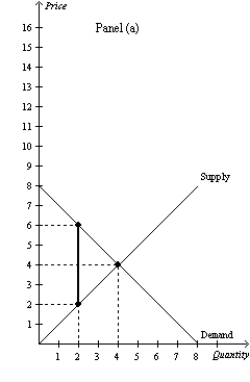
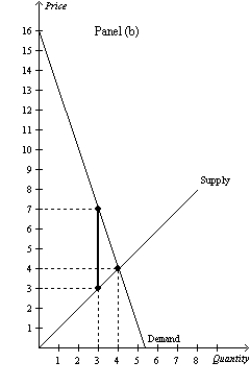
-Refer to Figure 8-15.Panel (a) and Panel (b) each illustrate a $4 tax placed on a market.In comparison to Panel (a) ,Panel (b) illustrates which of the following statements?
Definitions:
Cost Of Goods Sold
The expenses directly associated with the manufacturing of products sold by a business, which include the costs of both materials and labor.
Percentage Increase
A measure of how much a quantity has grown, expressed as a percentage of its previous value.
Financial Statement Analysis
The process of examining and interpreting a company’s financial statements to gauge its performance, strength, and profitability.
Circular Analysis
A method of analysis in which variables are interconnected through a series of equations, allowing for multiple variables to be solved simultaneously.
Q27: Refer to Figure 9-6. The amount of
Q75: Economists generally agree that the most important
Q109: Refer to Scenario 9-2. Suppose the world
Q110: When demand increases so that market price
Q271: Refer to Figure 7-34. Suppose the government
Q289: Suppose the demand curve and the supply
Q310: Refer to Figure 7-33. Suppose demand shifts
Q371: In a competitive market, sales go to
Q431: Suppose that the market for large, 64-ounce
Q466: Refer to Figure 9-9. Total surplus in