Scenario 9-2
• For a small country called Boxland,the equation of the domestic demand curve for
cardboard is  ,
,
where 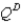 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and 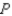 represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
• For Boxland,the equation of the domestic supply curve for cardboard is 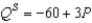 ,
,
where 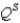 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and 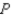 again
again
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-Refer to Scenario 9-2.Suppose the world price of cardboard is $45 and international trade is allowed.Then Boxland's consumers demand
Definitions:
Exchange Rate
The rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another, often influencing international trade and investments.
Exchange Rates
The rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another.
Meals
Prepared food items meant for immediate consumption.
Tours
Organized trips or excursions, often for leisure, education, or cultural purposes.
Q55: Refer to Figure 10-15. The supply of
Q61: Most economists prefer corrective taxes to regulation
Q187: Suppose that a firm produces electricity by
Q298: Refer to Figure 9-22. With free trade,
Q374: Refer to Scenario 9-2. Suppose the world
Q414: As the size of a tax rises,
Q414: The United States has imposed taxes on
Q423: Refer to Figure 10-9. The overuse of
Q446: Suppose planting flowering shrubs creates a positive
Q493: If gasoline taxes were significantly increased in