Figure 34-2. On the left-hand graph, MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph, AD represents aggregate demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
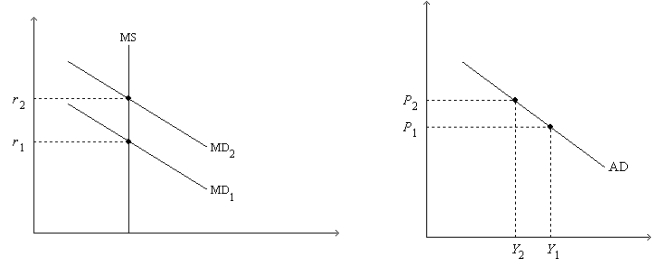
-Refer to Figure 34-2. Assume the money market is always in equilibrium. Under the assumptions of the model,
Definitions:
Standard Quantity
The predetermined amount of materials or resources expected to be used in the production of a product.
Variable Manufacturing Overhead
Indirect production costs that fluctuate with the level of output, including utilities and supplies that vary with production volume.
Labor Rate Variance
The difference between the actual hourly labor rate and the standard rate, multiplied by the number of hours worked during the period.
Overhead Rate Variance
Overhead Rate Variance is the difference between the actual overhead costs incurred and the overhead costs allocated based on a predetermined rate.
Q62: Liquidity refers to<br>A) the relation between the
Q71: Which of the following is likely more
Q133: When the money supply increases<br>A) interest rates
Q135: The theory of liquidity preference was developed
Q177: If the government cuts the tax rate,
Q349: The logic of the multiplier effect applies<br>A)
Q381: Which of the following policy alternatives would
Q440: When taxes decrease, consumption<br>A) increases, so aggregate
Q462: At a given price level, an increase
Q471: Sometimes, changes in monetary policy and/or fiscal