Different concentrations of ions on either side of a cell membrane constitute a concentration cell, which is described by the Nernst equation given below. A cell must expend energy to maintain this concentration gradient by moving ions from one side of the membrane to the other. How much energy must be expended to transport 1 mole of sodium ions across a membrane when the sodium ion concentration is 0.10 M on one side of the membrane and 0.010 M on the other side, and the temperature is 37°C (body temperature)?
(Given: Na+ + e- a, 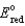 = -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K)
= -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K) 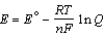
Definitions:
Inventory Purchases
The acquisition of goods and materials a company intends to sell in its ordinary course of business.
Beginning Inventory
The value of goods available for sale at the start of an accounting period.
Beginning Inventory
The value of all inventory held by a company at the start of an accounting period.
Gross Profit
Gross Profit is the financial metric calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total sales revenue.
Q4: Hydrated transition metal ions produce solutions that
Q31: Methanol fuel cells depend on the following
Q38: Plants react urea with water to produce
Q42: Eurodollar bonds are<br>A) purchased with dollars but
Q44: Pacemakers implanted in the chests of patients
Q80: Nuclear fusion produces energy because _<br>A) neutrons
Q97: Debentures are secured by<br>A) the issuer's good
Q102: The actual return on a bond is
Q104: Government securities money funds are structured to
Q126: The solubility product for an insoluble salt