Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide. The rate constant for the uncatalyzed reaction is 4.0 10-11/s at 22°C. Urease increases the rate constant to a value of 8.0 10-5/s. Use the Arrhenius equation, which is given below, to determine the difference in the activation energies Euncatalyzed - Ecatalyzed. (R = 8.315 J/mol K) 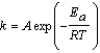
Definitions:
Deadlocked Corporation
A situation where the directors or shareholders of a corporation are unable to reach a consensus, halting decision-making processes.
Cohen v. Mirage Resorts, Inc.
A legal case that addresses issues related to securities law, potentially involving aspects of shareholder rights or corporate governance.
Dissenting Shareholder
A shareholder who disagrees with the direction or decision of the majority of the company's management or the outcome of a vote and formally records their dissent.
Derivative Suit
A lawsuit brought by a company shareholder on behalf of the corporation against a third party, often the company's executives or directors, for allegedly harming the company.
Q4: Mutual funds invest in diversified portfolios of
Q33: The duration of a bond portfolio is
Q53: A steep yield curve is generally considered
Q53: Stocks are a(n) _ investment representing _
Q63: Nitrogen-13 decays by positron emission to produce
Q67: What repulsive forces must be overcome for
Q70: Describe some of the relatively new investment
Q91: Which one of the following items does
Q102: Which of the following are not amino
Q113: Typical services offered by mutual funds include:<br>I.