Calculate the equilibrium constant at 500 K for the following reaction given the data below.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 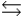 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
Kc(298 K) = 6.1 105
G  (NH3,g) = -16.5 kJ/mol
(NH3,g) = -16.5 kJ/mol
H  (NH3,g) = -46.1 kJ/mol
(NH3,g) = -46.1 kJ/mol
Definitions:
Interest in Land
A legal or equitable claim on real property, such as ownership, a mortgage, or a lease.
Primary Obligation
A primary obligation is the main responsibility or liability that a party is bound to fulfill under the terms of a contract or agreement.
Oral Sales Contract
A verbal agreement between parties for the purchase and sale of goods or services, which may be legally binding depending on the context and the nature of the transaction.
Enforceable
Refers to a legal agreement that can be upheld or compelled in a court of law.
Q44: A hydrogen fuel cell depends on _<br>A)
Q51: According to band theory, when the lower
Q62: When 1 mol of an alkene with
Q73: The reaction Cr(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>(aq) + 3<sup> </sup>en(aq) <font
Q74: The initial rate data for the reaction
Q84: A proposed mechanism for the reduction of
Q88: Which of the solutions shown here will
Q93: Which functional group is found in the
Q150: What is the concentration of [OH<sup>-</sup>] in
Q155: When [H<sup>+</sup>] = 1.0 <font face="symbol"></font> 10<sup>-</sup><sup>7</sup>