Use the relative energies of the molecular orbitals given below, which are derived from the n = 5 atomic orbitals, to determine the bond orders in I2 , 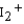 , and
, and 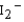 , and identify the species that is predicted to be the least stable. The valence molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy are < * < < < * <*.
, and identify the species that is predicted to be the least stable. The valence molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy are < * < < < * <*.
Definitions:
Reaction
A process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.
Acid Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a reaction by donating protons (H+) without being consumed in the process.
Reaction
A chemical process in which substances interact to form new products, involving changes in chemical bonds.
Cyanohydrin
Organic compounds with a nitrile and a hydroxyl functional group attached to the same carbon atom.
Q4: What physical property is used to separate
Q7: Two identical cement blocks are placed on
Q9: Which of the following molecules is paramagnetic?<br>A)
Q40: What wavelength of light is required to
Q50: Hard water contains Mg<sup>2+</sup> and Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions
Q61: Electronegativity increases from left to right across
Q76: If 50.0 mL of a 0.10 M
Q82: The atmospheric pressure in the eye of
Q83: Arrange the first four halogens in order
Q103: Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs or freons) are linked to