When equal volumes of the indicated solutions are mixed, precipitation should occur only for: 
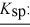 barium fluoride 1.0 × 10-6 calcium carbonate 2.8 × 10-9
barium fluoride 1.0 × 10-6 calcium carbonate 2.8 × 10-9
Calcium fluoride 5.3 × 10-9
Magnesium fluoride 3.7 × 10-8
Silver carbonate 8.5 × 10-12
Definitions:
Significant Correlation
Significant correlation refers to a statistical relationship between two variables that is unlikely to have occurred by chance, indicating a meaningful association.
Causal Relationship
A relationship between variables in which changes in one variable demonstrably result in changes in another.
Type I Error
The incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis, often referred to as a "false positive."
Confidence Interval
A statistical range, based on sample data, within which there is a specified probability that the value of a parameter lies.
Q1: Choose the INCORRECT statement.<br>A) The Frasch process
Q6: How will addition of sodium acetate to
Q12: What is ΔG°rxn? <br>CO(g) + 2 H<sub>2</sub>(g)
Q18: A concentrated buffer of pH 8.0 is
Q25: A weak acid has Ka = 4.2
Q50: Hydrogen bonded with any metals form compounds
Q57: A solution prepared by dissolving 4.00 g
Q79: What is the pH of a solution
Q85: A pH 9.56 buffer was prepared by
Q94: On the average, air contains about 9.3