For the reaction
2NO(g) + H2(g) N2O(g) + H2O(g)
two mechanisms, A and B, have been proposed. Derive the rate law for each proposed mechanism for the production of N2O. 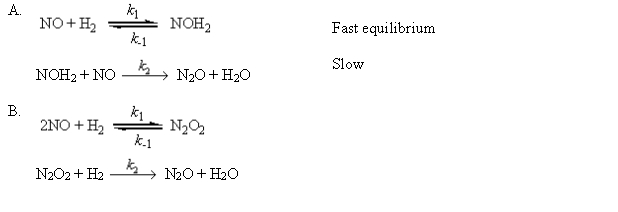 For mechanism B, use the steady-state approximation. Let rate
For mechanism B, use the steady-state approximation. Let rate 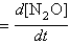
Definitions:
Supply Chain Management
The active management of supply chain activities to maximize customer value and achieve a sustainable competitive advantage, encompassing everything from production to product delivery.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, with cost per unit of output generally decreasing with increasing scale.
Pull Strategy
A supply chain strategy in which customer orders drive manufacturing and distribution operations.
Transportation Management
The process of planning, executing, and optimizing the movement of goods and materials from their point of origin to their final destination.
Q13: Calculate <font face="symbol"></font>S for an isothermal (95°C)
Q17: Oxygen is paramagnetic and has a bond
Q22: A 54.4-g sample of glucose (a nondissociated,
Q42: The configuration (<font face="symbol"></font><sub>2s</sub>)<sup>2</sup>(<font face="symbol"></font><sub>2s</sub>*)<sup>2</sup>(<font face="symbol"></font><sub>2py</sub>)<sup>1</sup>(<font face="symbol"></font><sub>2px</sub>)<sup>1</sup>
Q49: Within the halogen family, as atomic number
Q58: The following reaction occurs in basic solution:
Q75: For the reaction in the presence
Q76: The volume of a single cell<br>A) 1.20
Q81: In which case must a reaction be
Q133: How many of the following molecules and