Calculate ΔG° for 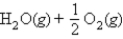

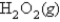
At 600. K, using the following data:
H2(g) + O2(g)  H2O2 Kp = 2.3 × 106 at 600.
H2O2 Kp = 2.3 × 106 at 600.
K2H2(g) + O2(g)  2H2O(g) Kp = 1.8 × 1037 at 600. K
2H2O(g) Kp = 1.8 × 1037 at 600. K
Definitions:
Variable
An element, feature, or factor that is liable to vary or change, often used in scientific research to measure and analyze differences.
Identical
Exactly the same, alike in every way. This term is often used to describe objects, twins, or situations that are indistinguishable from each other.
Statistically Significant
A term used to denote a result that is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a predetermined threshold of probability.
Francophone Canadians
French-speaking Canadians, primarily concentrated in Quebec but also found throughout the country, possessing a distinct culture and identity.
Q8: ΔS<sub>univ</sub><br>A) 0<br>B) -79.6 J/K•mol<br>C) 79.6 J/K•mol<br>D) -103
Q11: In which direction do electrons flow in
Q26: Methyl orange is an indicator with a
Q30: Calculate [OH<sup>-</sup>] in a 4.0 × 10<sup>-8</sup>
Q36: A strip of copper is placed in
Q46: An element E has the electron configuration
Q65: Which of the following are state functions?<br>A)
Q79: A bomb calorimeter has a heat capacity
Q87: The sodium salt, NaA, of a weak
Q93: ΔE is<br>A) greater than zero.<br>B) less than