The Stanford linear accelerator contains hundreds of brass disks tightly fitted into a steel tube (see figure) . The coefficient of linear expansion of the brass is 2.00 *10-5 per C . The system was assembled by cooling the disks in dry ice (-57 C) to enable them to just slide into the close-fitting tube. If the diameter of a disk is 80.00 mm at 43 C, what is its diameter in the dry ice? 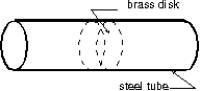
Definitions:
Simple Cuboidal
Epithelial cells shaped like cubes or squares; these cells are found in glands and ducts and function in secretion or absorption.
Epithelium
a layer of cells forming the epidermis of the skin and the surface layer of mucous and serous membranes, playing roles in protection, secretion, and absorption.
Flat Cells
Cells that are flattened in shape, often found lining surfaces such as the skin or blood vessels, contributing to the formation of epithelial tissues.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue is a layer of cells that forms the outer covering of the body and the lining of internal organs and structures, serving protective, absorptive, and secretory functions.
Q1: For a cylindrical resistor made of ohmic
Q9: Two small identical speakers are connected (in
Q11: One piston in a hydraulic lift
Q36: A string of length L is clamped
Q38: A man, holding a weight in each
Q44: An isothermal process for an ideal gas
Q45: Resistor 1 has twice the resistance of
Q48: A certain x-ray tube requires a current
Q48: The elliptical orbit of a planet around
Q53: A particle is in simple harmonic motion