The potential energy for the interaction between the two atoms in a diatomic molecule is U = A/x12 - B/x6, where A and B are constants and x is the interatomic distance. The magnitude of the force of one atom exerts on the other is: 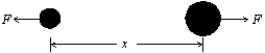
Definitions:
Repressor Protein
A protein that binds to specific DNA sequences and inhibits the expression of a gene by blocking the action of RNA polymerase.
Transcription
The process by which the genetic information in DNA is copied to messenger RNA (mRNA), initiating protein synthesis.
Repressors
Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences to inhibit the transcription of certain genes, regulating gene expression.
DNA Binding Sites
Specific sequences within a DNA molecule that are recognized and bound by other molecules, such as proteins, to regulate gene expression.
Q21: Which of the following bodies has the
Q22: The rotational inertia of a wheel about
Q28: A heavy wooden block is dragged by
Q28: A lead block is suspended from your
Q32: A particle moves along the x axis
Q37: An object moving in a circle at
Q44: A block with mass M, on the
Q53: The coordinate of an object is given
Q57: Which of the following is NOT added
Q70: The fan shown has been turned