A heat engine in each cycle absorbs energy of magnitude 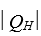 as heat from a high temperature reservoir, does work of magnitude
as heat from a high temperature reservoir, does work of magnitude 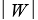 , and then absorbs energy of magnitude
, and then absorbs energy of magnitude 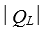 as heat from a low temperature reservoir.If
as heat from a low temperature reservoir.If 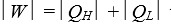 this engine violates:
this engine violates:
Definitions:
Variable Costing
An accounting method that includes only variable production costs (materials, labor, and overhead) in product costs and treats fixed overhead costs as period costs.
Absorption Costing
An accounting method that incorporates all direct and indirect manufacturing costs into the cost of a product.
Net Profit
The total earnings of a company after subtracting all expenses, including taxes and operating costs, from its total revenues.
Variable Manufacturing Costs
Expenses that fluctuate with production output levels, including raw materials, direct labor, and utility costs directly involved in the manufacturing process.
Q9: The electric field at a distance of
Q18: A hollow conductor is positively charged. A
Q20: Two wires made of different materials have
Q22: A Carnot cycle heat engine operates between
Q28: The electric field due to a uniform
Q36: An electron and a proton both each
Q42: A beam of electrons is sent horizontally
Q45: In the diagrams, all light bulbs are
Q66: The number of degrees of freedom of
Q95: The force on the walls of a