The following equations represent a simultaneous equations model: K1 =  1K2 +
1K2 + 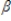 1z1 + u1
1z1 + u1
K2 =  2K1+
2K1+ 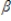 2z2 + u2
2z2 + u2
The reduced form equation for K2 will express:
Definitions:
Preconventional Morality
Preconventional morality is the first level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development, where moral understanding is based on rewards and punishments.
Menarche
The first occurrence of menstruation in a female, symbolizing the onset of reproductive ability.
Identity
The qualities, beliefs, personality, looks, and expressions that make a person (self-identity) or group (particular social category or social group).
Integrity
The quality of being honest and having strong moral principles, or the state of being whole and undivided.
Q1: How many atoms are present in a
Q2: In time series regressions, it is advisable
Q4: The income of an individual in Budopia
Q11: For panel data, it is best if
Q21: The mixture of gas and air inside
Q22: If the explained sum of squares is
Q52: The compound MgF<sub>2 </sub>is composed of:<br>A) polyatomic
Q66: Which of the following scenarios does not
Q68: When hiring people who are beginning their
Q112: Understanding _ helps a manager know which