The following equations represent a simultaneous equations model: K1 =  1K2 +
1K2 + 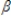 1z1 + u1
1z1 + u1
K2 =  2K1+
2K1+ 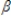 2z2 + u2
2z2 + u2
OLS will suffer from simultaneity bias if:
Definitions:
Tax Avoidance
The legal use of tax laws to reduce one's tax burden through various means and financial arrangements.
Tax System Equity
The fairness of a tax system, assessed by how the tax burden is distributed among different groups in society.
Deadweight Losses
Economic inefficiencies that occur when the allocation of resources is not optimal, typically due to market imbalances or government interventions.
Tax
A compulsory financial charge or other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures.
Q4: Consider the following regression model: log(y) =
Q6: Which element will float on pure water?<br>A)
Q7: A data set is called an unbalanced
Q11: An explanatory variable is said to be
Q17: Consider the following simple regression model: y
Q22: Which of the following assumptions is known
Q29: F,Cl,and Br all belong to what family?<br>A)
Q37: When heated,iron and sulfur combine to form
Q108: If innovation is the introduction of new
Q111: _ is specifying the goals to be