The following equations represent a simultaneous equations model: K1 =  1K2 +
1K2 + 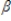 1z1 + u1
1z1 + u1
K2 =  2K1+
2K1+ 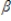 2z2 + u2
2z2 + u2
The reduced form equation for K2 will express:
Definitions:
Advanced Old Age
Advanced old age refers to a late stage in an individual's life, often characterized by increased dependency due to physical or cognitive decline.
Declarative Memory
Declarative memory is a type of long-term memory that involves the conscious recollection of factual information, experiences, and concepts, also known as explicit memory.
Episodic Memory
A type of long-term memory that involves the recollection of specific events, situations, and experiences.
Anterograde Amnesia
A condition where an individual is unable to form new memories following the onset of an amnesia-causing event, although memories from before the event remain intact.
Q7: In a natural experiment, the same cross-sectional
Q15: Time series regression is based on series
Q16: For 2.5% significance level, the asymptotic critical
Q16: What are the four principles of scientific
Q18: Which configuration describes the electron configuration of
Q21: How many molecules of carbon monoxide,CO,comprise 2.34
Q22: When a metal and a nonmetal combine,they
Q56: How many valence electrons does a neutral
Q73: Taylor's theory is criticized because it<br>A) ignored
Q107: _ involves monitoring performance and making necessary