Consider the following simple regression model y = 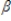 0 +
0 + 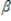 1x1 + u. Suppose z is an instrument for x. if Cov(z,u) = 0 and Cov(z,x)
1x1 + u. Suppose z is an instrument for x. if Cov(z,u) = 0 and Cov(z,x) 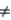 0, the value of
0, the value of 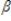 1 in terms of population covariances is _____.
1 in terms of population covariances is _____.
Definitions:
Lack of Experience
The absence or deficiency of practical contact with, and observation of facts or events in a particular field.
Business Operations
Encompasses all the activities and tasks that a business engages in on a day-to-day basis to run smoothly and efficiently, delivering goods or services to customers.
Essentials
Fundamental elements or components necessary for the basic functioning or success of a system, organization, or activity.
Succession Plan
A strategy for identifying and developing new leaders who can replace old leaders when they leave, retire, or die, to ensure organizational continuity.
Q1: The average treatment effect measures _.<br>A)the effect
Q2: The square root of the quantity <img
Q5: A bomb calorimeter has a heat capacity
Q5: Two stage least squares estimation cannot be
Q8: Which formula is the CORRECT one for
Q12: Two equations form a nonnested model when:<br>A)one
Q17: Which nuclide is represented by the atomic
Q21: If the data are missing at random,
Q26: Which subatomic particle has the GREATEST mass?<br>A)
Q55: When two nonmetals combine,they "share" the electrons