A vector 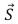 of magnitude 6 and another vector
of magnitude 6 and another vector 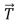 have a resultant of magnitude 12.The vector
have a resultant of magnitude 12.The vector 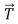 :
:
Definitions:
Trademark Infringement
The unauthorized use of a trademark or service mark on or in connection with goods and/or services in a manner that is likely to cause confusion, deception, or mistake about the source of the goods and/or services.
Likelihood of Confusion
This refers to a standard used in trademark law to assess whether the similarity between two marks is likely to confuse consumers about the source of the products or services.
Trade Secret
A form of intellectual property comprising confidential information that provides a business with a competitive edge.
Sufficient Value
A concept in contract law that refers to the necessity of both parties exchanging something of value for a contract to be considered valid.
Q3: A sledge (including load)weighs 5000 N.It is
Q13: Compared to other adults in the U.S.,_
Q24: Baruque scores very high on the personality
Q27: A heavy ball is suspended as shown.A
Q29: A 6-kg object is moving south.A net
Q44: The diagram shows a plot of the
Q49: The center of mass of a system
Q50: A block slides down a frictionless plane
Q52: The coordinate of an object is given
Q57: A 1000-kg space probe is motionless in