A small disk of radius R1 is mounted coaxially with a larger disk of radius R2.The disks are securely fastened to each other and the combination is free to rotate on a fixed axle that is perpendicular to a horizontal frictionless table top, as shown in the overhead view below.The rotational inertia of the combination is I.A string is wrapped around the larger disk and attached to a block of mass m, on the table.Another string is wrapped around the smaller disk and is pulled with a force 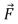 as shown.The acceleration of the block is:
as shown.The acceleration of the block is: 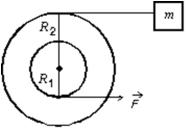
Definitions:
Equivalent Units
A concept used in cost accounting to express the amount of goods or services produced in terms of the number of complete units.
Materials
The raw items and components used in the production of goods.
Process Costing
An accounting methodology used for homogeneous products, attributing costs to units of product through an average or a similar method.
Conversion Costs
The combined costs of direct labor and manufacturing overhead expenses, representing the costs necessary to convert raw materials into finished goods.
Q7: The pull P is just sufficient to
Q12: A mass m is located at the
Q12: An 8-N block slides down an incline.It
Q28: Which of the following groups does NOT
Q36: A 2.0-kg block travels around a 0.50-m
Q47: The force on a particle is given
Q49: No kinetic energy is possessed by:<br>A)a shooting
Q52: A 5.0-kg crate is on an incline
Q62: A sinusoidal wave is traveling toward the
Q71: A non-viscous incompressible liquid is flowing through