A heat engine in each cycle absorbs energy of magnitude 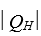 as heat from a high temperature reservoir, does work of magnitude
as heat from a high temperature reservoir, does work of magnitude 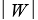 , and then absorbs energy of magnitude
, and then absorbs energy of magnitude 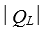 as heat from a low temperature reservoir.If
as heat from a low temperature reservoir.If 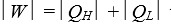 this engine violates:
this engine violates:
Definitions:
Task Times
The duration required to complete a specific task or activity within a process or project.
Stations Needed
The total number of workstations or production stations required to complete a job or to fulfill a specific part of a manufacturing process efficiently.
Cycle Time
The total time from the beginning to the end of a process, as measured by the customer.
Q4: The resonance condition in a cyclotron states
Q18: A series circuit consists of a battery
Q21: The quantity (1/2) <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\varepsilon"><span
Q28: A uniform electric field of 300 N/C
Q36: Twenty-five identical molecules are in a box.Microstates
Q48: In the context of the loop and
Q64: A disk whose rotational inertia is 450
Q91: During a slow adiabatic expansion of a
Q106: The temperature of n moles of
Q109: According to the kinetic theory of gases,