The diagram shows the graphs of the stopping potential as a function of the frequency of the incident light for photoelectric experiments performed on three different materials.Rank the materials according to the values of their work functions, from least to greatest. 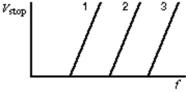
Definitions:
Conventional Charts
Traditional graphical representations of data, such as bar graphs, line charts, and pie charts, used to visualize information.
Line Charts
A type of chart that displays information as a series of data points connected by straight line segments, commonly used to visualize trends over time.
Vertical Axis
A line or scale along the side of a chart or graph that shows the value of something.
Horizontal Axis
In graphs and charts, the x-axis that runs left to right and typically represents the independent variable or time.
Q5: Binoculars and microscopes are frequently made with
Q12: A point source emits electromagnetic energy at
Q37: A convex spherical mirror has a focal
Q44: In a compound microscope, the objective has
Q50: In a nuclear power plant, the power
Q59: In the relation µ<sub>z</sub>=-m<sub> <span class="ql-formula"
Q60: A hollow lens is made of thin
Q61: The largest x-ray wavelength that can be
Q64: An erect object is 2f in front
Q65: Light with an intensity of 1 kW/m<sup>2</sup>