To examine the differences between salaries of male and female middle managers of a large bank,90 individuals were randomly selected,and two models were created with the following variables considered: Salary = the monthly salary (excluding fringe benefits and bonuses) ,
Educ = the number of years of education,
Exper = the number of months of experience,
Train = the number of weeks of training,
Gender = the gender of an individual;1 for males,and 0 for females.
Excel partial outputs corresponding to these models are available and shown below.
Model A: Salary = β0 + β1 Educ + β2 Exper + β3 Train + β4 Gender + ε 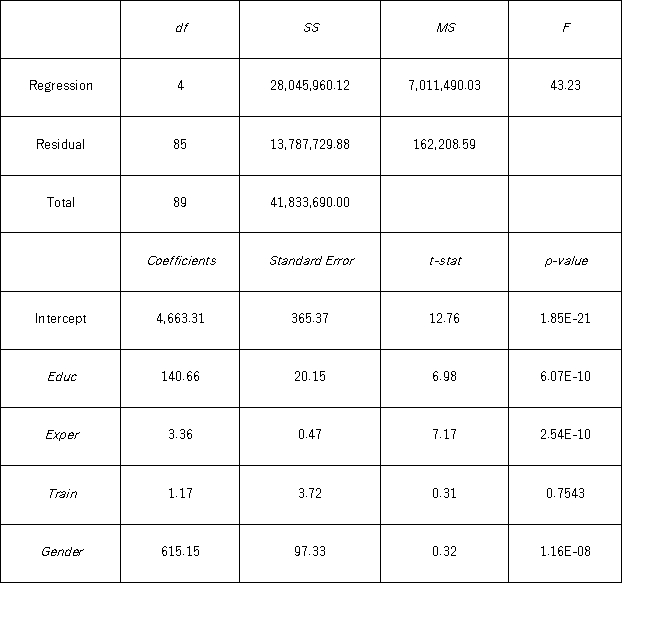 Model B: Salary = β0 + β1 Educ + β2 Exper + β3 Gender + ε
Model B: Salary = β0 + β1 Educ + β2 Exper + β3 Gender + ε 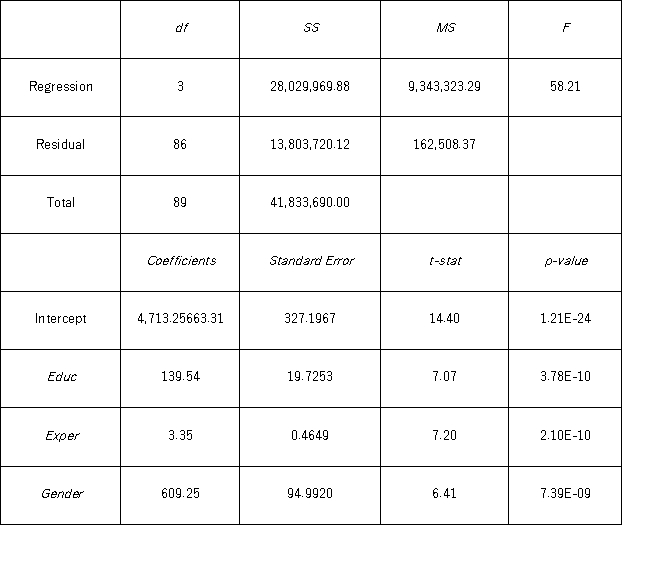 Under the assumption of the same years of education and months of experience,what is the null hypothesis for testing whether the mean salary of males is greater than the mean salary of females using Model B?
Under the assumption of the same years of education and months of experience,what is the null hypothesis for testing whether the mean salary of males is greater than the mean salary of females using Model B?
Definitions:
Standard Score
A statistical measure that indicates how many standard deviations an element is from the mean of its distribution.
Raw Score
The initial, unadjusted score obtained directly from a test or assessment before any transformations or normative comparisons.
Assessing Reliability
The process of determining the consistency and stability of a measurement tool or test over time.
Internal Consistency
A measure of reliability which evaluates how strongly items in an assessment are related in a single administration.
Q22: Which of the following regression models is
Q25: A sociologist estimates the regression relating Poverty
Q30: Consider the following price (in dollars)and quantity
Q36: Consider the following information about the price
Q47: The linear and logarithmic models,y = β<sub>0</sub>
Q60: A gender is an example of _
Q90: The income component is _ for stocks,interest
Q96: It is believed that the sales volume
Q109: To examine the differences between salaries of
Q110: An economist estimates the following model: y