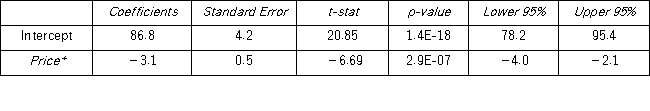
A marketing manager examines the relationship between the attendance at amusement parks and the price of admission.He estimates the following model: Attendance = β0 + β1 price + ε,where Attendance is the average daily number of people who attend an amusement park in July (in 1,000s)and Price is the price of admission.The marketing manager would like to construct interval estimates for Attendance when Price equals $80.The researcher estimates a modified model where Attendance is the response variable and the Price is now defined as Price* = Price - 80.A portion of the regression results is shown in the accompanying table. 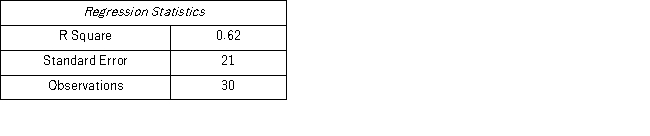
 a.According to the modified model,what is the point estimate for Attendance when Price equals $80?
a.According to the modified model,what is the point estimate for Attendance when Price equals $80?
b.According to the modified model,what is a 95% confidence interval for Attendance when Price equals $80? (Note that t0.025,28 = 2.048. )
c.According to the modified model,what is a 95% prediction interval for Attendance when Price equals $80? (Note that t0.025,28 = 2.048. )
Definitions:
Weighted-Average Method
This inventory costing method assigns the average cost of goods available for sale during the period to both ending inventory and cost of goods sold.
Equivalent Unit
A calculation used in cost accounting that converts partially completed goods into a number of complete units of output, helping in the costing process of production.
Weighted-Average Method
An inventory costing method that calculates the cost of goods sold and ending inventory based on the average cost of all units available during the period.
Units Transferred
The quantity of goods moved from one process, department, or location to another within a company's operations.
Q4: A sociologist wishes to study the relationship
Q15: For a sample of 10 observations drawn
Q26: A university has six colleges and takes
Q51: In the following table,likely voters' preferences of
Q55: Like any other university,Seton Hall University uses
Q58: Consider the expected returns (in percent)from the
Q71: A professor applies the variance in scores
Q85: The following table shows the distribution of
Q89: The income yield from a one-year infrastructure
Q91: The coefficient of determination R<sup>2</sup> cannot be