A financial analyst examines the performance of two mutual funds and claims that the variances of the annual returns for the bond funds differ.To support his claim,he collects data on the annual returns (in percent) for the years 2001 through 2010.The analyst assumes that the annual returns for the two emerging market bond funds are normally distributed.Use the following summary statistics. 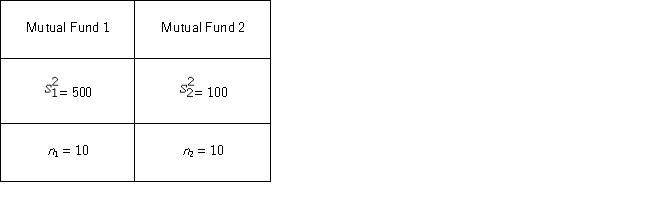 The competing hypotheses are
The competing hypotheses are 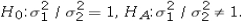 Which of the following is the critical F value at the 10% significance level?
Which of the following is the critical F value at the 10% significance level?
Definitions:
Equation of Exchange
An economic formula representing the relationship between the money supply, the velocity of money, the price level, and the number of transactions in an economy.
Money Supply
The entire stock of money assets in an economy at a specified period.
Velocity of Money
The rate at which money is exchanged in an economy and is used to measure the activity level of economic transactions.
Nominal Gross Domestic Product
The total market value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific time period, evaluated at current market prices without adjusting for inflation.
Q18: The formula for the confidence interval of
Q38: Which of the following is not a
Q39: The mortgage foreclosure crisis that preceded the
Q63: The student senate at a local university
Q65: Over the past 30 years,the sample standard
Q79: When conducting a hypothesis test,which of the
Q81: Which of the following is the formula
Q83: In a multiple regression based on 30
Q85: Which of the following identifies the range
Q100: What conditions are required by the central