Keynes postulated that the marginal propensity to consume (MPC = 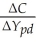 )is between zero and one.He also hypothesized that the average propensity to consume (APC =
)is between zero and one.He also hypothesized that the average propensity to consume (APC = 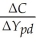 )would fall as personal disposable income
)would fall as personal disposable income 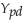 increased.
increased.
(a)Specify a linear consumption function.Show that the assumption of a falling APC implies the presence of a positive intercept.
(b)Using annual per capita data,estimation of the consumption function for the United States results in the following output for the years 1929-1938: 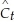 = 981.35 + 0.735
= 981.35 + 0.735 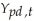 ,R2 = 0.98,SER= 50.65
,R2 = 0.98,SER= 50.65
(158.65)(0.038)
Can you reject the null hypothesis that the slope is less than one? Greater than zero? Test the hypothesis that the intercept is zero.Should you be concerned about the sample size when conducting these tests? What other threats to internal validity may be present here?
(c)Given the GDP identity for a closed economy, 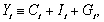 show why economists saw important policy implications in finding an APC that would decrease over time.
show why economists saw important policy implications in finding an APC that would decrease over time.
(d)Simon Kuznets,who won the Nobel Prize in economics,collected data on consumption expenditures and national income from 1869 to 1938 and found,using overlapping period averages,that the APC was relatively constant over this period.To reconcile this finding with the regression results,Milton Friedman,who also won the Nobel Prize,formulated the "permanent income" hypothesis.In essence,Friedman hypothesized that both actual consumption and income are measured with error, 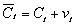 and
and 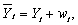 where
where 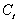 and
and 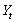 were called "permanent" consumption and income,respectively,and
were called "permanent" consumption and income,respectively,and 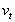 and
and 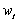 ,the two measurement errors,were labeled transitory consumption and income.Friedman hypothesized that the transitory components were purely random error terms,uncorrelated with the permanent parts.
,the two measurement errors,were labeled transitory consumption and income.Friedman hypothesized that the transitory components were purely random error terms,uncorrelated with the permanent parts.
Let permanent consumption and income be related as follows: 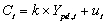 so that the APC and MPC are the same and constant over time.Furthermore,let both transitory and permanent income be independent of the error term.Show that by regressing actual consumption on actual income,the MPC will be downward biased,and the intercept will be greater than zero,even in large samples (to simplify the analysis,assume that permanent income and all of the errors are i.i.d.and mutually independent).
so that the APC and MPC are the same and constant over time.Furthermore,let both transitory and permanent income be independent of the error term.Show that by regressing actual consumption on actual income,the MPC will be downward biased,and the intercept will be greater than zero,even in large samples (to simplify the analysis,assume that permanent income and all of the errors are i.i.d.and mutually independent).
Definitions:
Average Total Cost
The cost per unit of output, calculated by dividing the total production cost by the quantity of output produced.
Marginal Revenue
The supplementary earnings acquired from selling an extra unit of a product or service.
Competitive Market
A market structure where multiple firms are vying for consumers' business, thereby fostering innovation and fair pricing due to competition.
Total Revenue
The full amount of capital a business garners from the sale of goods or the rendering of services for a particular timeframe.
Q7: You have collected data from Major League
Q8: An extension of the Solow growth model
Q14: From the Stock and Watson (http://www.pearsonhighered.com/stock_watson)website the
Q19: You have obtained a sample of 14,925
Q21: Which of the following instruments could be
Q25: Options traders who hold their positions for
Q28: When pursuing portfolio insurance of a stock
Q38: One of the advantages of forward markets
Q39: You have estimated the relationship between testscores
Q56: The following are all least squares assumptions