Your textbook gives the following example of simultaneous causality bias of a two equation system:
Yi = β0 + β1Xi + ui
Xi = 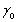 +
+ 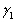 Yi + vi
Yi + vi
In microeconomics,you studied the demand and supply of goods in a single market.Let the demand ( 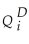 )and supply (
)and supply ( 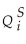 )for the i-th good be determined as follows,
)for the i-th good be determined as follows, 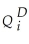 = β0 - β1Pi + ui,
= β0 - β1Pi + ui, 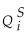 =
= 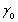 -
- 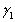 Pi + vi,
Pi + vi,
where P is the price of the good.In addition,you typically assume that the market clears.
Explain how the simultaneous causality bias applies in this situation.The textbook explained a positive correlation between Xi and ui for  > 0 through an argument that started from "imagine that ui is negative." Repeat this exercise here.
> 0 through an argument that started from "imagine that ui is negative." Repeat this exercise here.
Definitions:
Marginal Cost
The additional cost incurred to produce one more unit of a good or service, important for decision-making in production and pricing strategies.
Avid Runner
An individual who is highly passionate and consistent about running as a form of exercise or sport.
Opportunity Costs
The value of the best alternative forgone when a different investment or decision is made.
Productive Efficiency
A situation in which an economy or a production process can no longer produce additional amounts of a good without lowering the production level of another product, effectively utilizing all resources.
Q9: The settlement period in a swap refers
Q16: The adjusted R2,or <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="The adjusted
Q18: Which of the following statements is correct
Q19: Companies can benefit from risk management if
Q20: The price sensitivity hedge ratio uses the
Q22: Determine the value of an interest rate
Q27: Interest-only strips lose the some or all
Q43: Stress testing allows a firm to see
Q52: If the insured portfolio were dynamically hedged
Q60: To standardize a variable you<br>A)subtract its mean