An extension of the Solow growth model that includes human capital in addition to physical capital, suggests that investment in human capital (education) will increase the wealth of a nation (per capita income). To test this hypothesis, you collect data for 104 countries and perform the following regression: 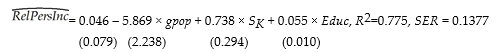
where RelPersInc is GDP per worker relative to the United States, gpop is the average population growth rate, 1980 to 1990, sK is the average investment share of GDP from 1960 to 1990, and Educ is the average educational attainment in years for 1985. Numbers in parentheses are for heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors.
(a) Interpret the results and indicate whether or not the coefficients are significantly different from zero. Do the coefficients have the expected sign?
(b) To test for equality of the coefficients between the OECD and other countries, you introduce a binary variable (DOECD), which takes on the value of one for the OECD countries and is zero otherwise. To conduct the test for equality of the coefficients, you estimate the following regression:
Write down the two regression functions, one for the OECD countries, the other for the non-OECD countries. The F- statistic that all coefficients involving DOECD are zero, is 6.76. Find the corresponding critical value from the F table and decide whether or not the coefficients are equal across the two sets of countries.
(c) Given your answer in the previous question, you want to investigate further. You first force the same slopes across all countries, but allow the intercept to differ. That is, you reestimate the above regression 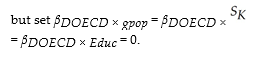
The t-statistic for DOECD is 4.39. Is the coefficient, which was 0.241, statistically significant?
(d) Your final regression allows the slopes to differ in addition to the intercept. The F-statistic for 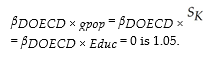
What is your decision? Each one of the t-statistics is also smaller than the critical value from the standard normal table. Which test should you use?
(e) Looking at the tests in the two previous questions, what is your conclusion?
Definitions:
Operations
The day-to-day activities involved in the running of a business for the purpose of producing value for the stakeholders; focuses on manufacturing and service processes.
Leadership and Navigation
The ability to direct and influence others towards achieving organizational goals while successfully navigating through complexity, change, or challenge.
HR Function
Comprises various roles and responsibilities within an organization to manage and support its workforce effectively.
Values and Behaviors
The beliefs and actions that are important to an individual or group, guiding their decisions and interactions.
Q3: The multiple regression model in matrix form
Q4: Enterprise risk management includes all of the
Q17: When there are omitted variables in the
Q24: Which of the following are advantages of
Q31: Until about 10 years ago,most studies in
Q38: When you have an omitted variable problem,the
Q38: The WLS estimator is called infeasible WLS
Q47: Under SEC rules,derivatives activities must be disclosed
Q49: The advantage of using heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors
Q59: SAT scores in Mathematics are normally distributed