Females,it is said,make 70 cents to the dollar in the United States.To investigate this phenomenon,you collect data on weekly earnings from 1,744 individuals,850 females and 894 males.Next,you calculate their average weekly earnings and find that the females in your sample earned $346.98,while the males made $517.70.
(a)Calculate the female earnings in percent of the male earnings.How would you test whether or not this difference is statistically significant? Give two approaches.
(b)A peer suggests that this is consistent with the idea that there is discrimination against females in the labor market.What is your response?
(c)You recall from your textbook that additional years of experience are supposed to result in higher earnings.You reason that this is because experience is related to "on the job training." One frequently used measure for (potential)experience is "Age-Education-6." Explain the underlying rationale.Assuming,heroically,that education is constant across the 1,744 individuals,you consider regressing earnings on age and a binary variable for gender.You estimate two specifications initially: 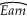 = 323.70 + 5.15 × Age - 169.78 × Female,R2=0.13,SER=274.75
= 323.70 + 5.15 × Age - 169.78 × Female,R2=0.13,SER=274.75
(21.18)(0.55)(13.06) 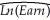 = 5.44 + 0.015 × Age - 0.421 × Female,R2=0.17,SER=0.75
= 5.44 + 0.015 × Age - 0.421 × Female,R2=0.17,SER=0.75
(0.08)(0.002)(0.036)
where Earn are weekly earnings in dollars,Age is measured in years,and Female is a binary variable,which takes on the value of one if the individual is a female and is zero otherwise.Interpret each regression carefully.For a given age,how much less do females earn on average? Should you choose the second specification on grounds of the higher regression R2?
(d)Your peer points out to you that age-earning profiles typically take on an inverted U-shape.To test this idea,you add the square of age to your log-linear regression. 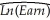 = 3.04 + 0.147 × Age - 0.421 × Female - 0.0016 Age2,
= 3.04 + 0.147 × Age - 0.421 × Female - 0.0016 Age2,
(0.18)(0.009)(0.033)(0.0001)
R2 = 0.28,SER = 0.68
Interpret the results again.Are there strong reasons to assume that this specification is superior to the previous one? Why is the increase of the Age coefficient so large relative to its value in (c)?
(e)What other factors may play a role in earnings determination?
Definitions:
Lifetime Learning Credit
A tax credit available in the United States for qualified tuition and related expenses paid for eligible students enrolled in an eligible educational institution, aiming to promote post-secondary education.
Tax Advantage
Financial benefits and savings provided through exemptions, deductions, and credits that reduce the amount of tax owed.
Earned Income Credit
A refundable tax credit for low to moderate-income working individuals and families, aimed at decreasing the amount of tax owed and potentially returning money to the taxpayer.
Inflation
The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, eroding purchasing power.
Q4: Math SAT scores (Y)are normally distributed with
Q12: A type II error<br>A)is typically smaller than
Q27: When testing joint hypothesis,you should<br>A)use t-statistics for
Q29: Several authors have tried to measure the
Q36: Imagine you regressed earnings of individuals on
Q40: The central limit theorem states that<br>A)the sampling
Q49: Since it states that systematic risk cannot
Q51: (Requires Appendix material)A necessary and sufficient condition
Q58: One of the following steps is not
Q61: Consider the population regression of log earnings